
These can include blood smears, where a film of your blood is examined under a microscope. Depending on the results, they may need to order additional tests. Your doctor will discuss any abnormal results with you. Other potential reasons for an elevated RBC count include: Tell your doctor about any medications you take. performance-enhancing drugs, like anabolic steroids or protein injections.methyldopa, often used to treat high blood pressure.gentamicin, an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections in the blood.certain tumors, like renal cell carcinoma or hepatocellular carcinomaĬertain drugs can increase your RBC count, including:.renal disorders, such as cysts or kidney disease.respiratory disorders, like COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, or sleep apnea.Some medical conditions that can cause a high red blood cell count include: This could be due to a disease, drug, or another cause. Secondary erythrocytosis is when an external factor increases your RBC count. One such condition is polycythemia vera, a bone marrow disease that causes overproduction of RBCs and is associated with a genetic mutation. This is usually due to a problem with cells in your bone marrow. Primary erythrocytosis is when your own body causes you to produce more RBCs. This causes your blood to be thicker than normal and can increase your risk of blood clots. If your RBC count is higher than normal, you have erythrocytosis. What does a higher than normal RBC count mean? hydantoins, traditionally used to treat epilepsy and muscle spasms.quinidine, which can treat irregular heartbeats.chloramphenicol, which treat bacterial infections.Other possible reasons for a lower than normal RBC count include:Ĭertain drugs can also lower your RBC count, especially: IBD, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.cancers, like leukemia or multiple myeloma.autoimmune diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.Other chronic conditions that may cause a low RBC count include, but are not limited to: If you have chronic kidney disease, you might produce less EPO than normal. EPO is a hormone that causes bone marrow to produce RBCs.ĮPO is produced in the kidneys. Underlying health conditions that cause inflammation may affect the way your body processes erythropoietin (EPO). inherited conditions, like sickle cell anemia.autoimmune reaction to blood transfusion.Hemolysis is the destruction of red blood cells. Certain drugs, viruses, toxins, or radiation may also cause aplastic anemia. This is caused aplastic anemia.Īplastic anemia might be an autoimmune disorder. In rare cases, your bone marrow might stop making new blood cells. Iron-deficiency anemia is the most common type of anemia, but lack of other nutrients can also cause your RBC count to decrease. There are many possible causes for anemia. This can be caused by a decrease in RBC production or by the destruction or loss of RBCs.

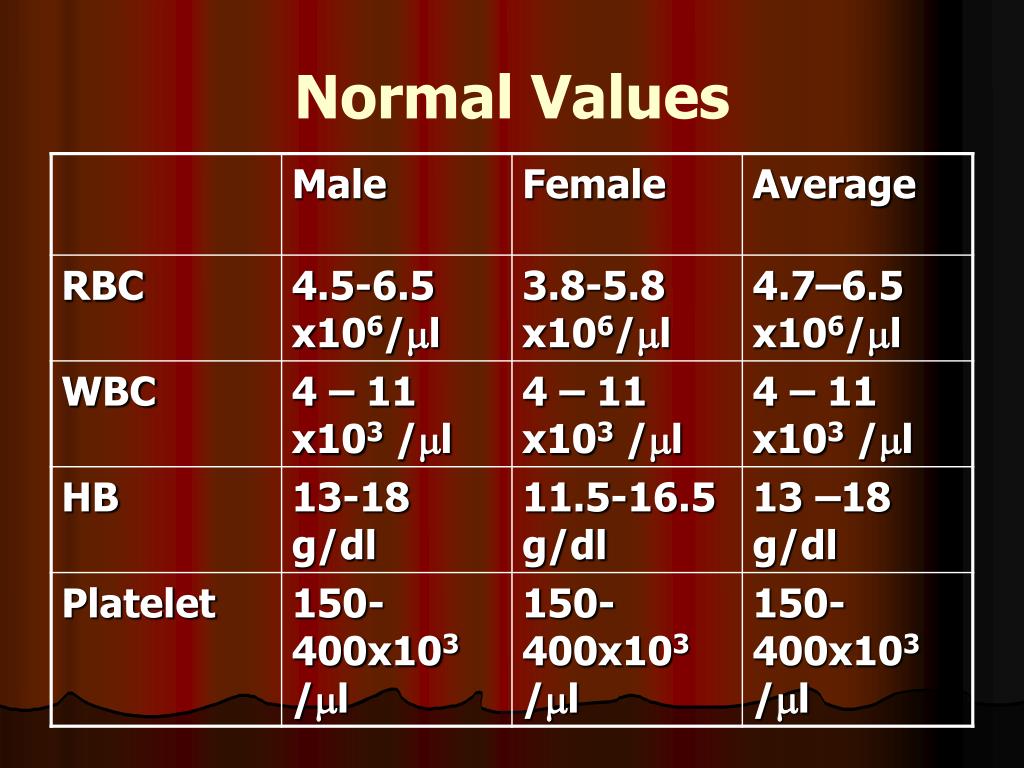
If your number of RBCs is lower than normal, you have anemia. What does a lower than normal RBC count mean? Doctors can use CBCs to monitor conditions like leukemia and infections of the blood. If you have a diagnosed blood condition that may affect RBC count, or you’re taking any medications that affect your RBCs, your doctor may order the test to monitor your condition or treatment. It may also be performed before a surgery. It can be an indicator of your overall health. These could include:Ī CBC will often be part of a routine physical exam. Your doctor may order the test if they suspect you have a condition that affects your RBCs, or if you show symptoms of low blood oxygen. Platelets are small cells that circulate in the blood and form blood clots that allow wounds to heal and prevent excessive bleeding. A hematocrit test measures the ratio of RBCs in your blood. Your hematocrit is the volume of red blood cells in your body. A CBC measures all components in the blood, including: According to the Association for Clinical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine, the test is almost always part of a complete blood count (CBC).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
